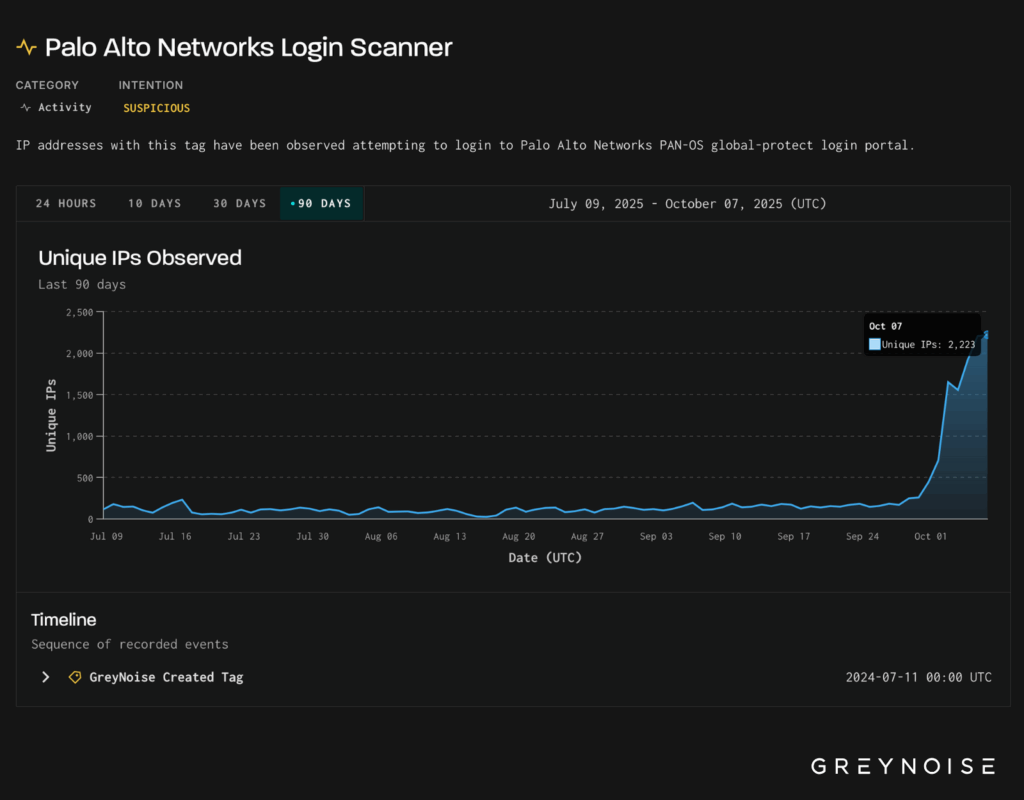
A massive escalation in attacks targeting Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS GlobalProtect login portals, with over 2,200 unique IP addresses conducting reconnaissance operations as of October 7, 2025.
This represents a significant surge from the initial 1,300 IPs observed just days earlier, marking the highest scanning activity recorded in the past 90 days according to GreyNoise Intelligence monitoring.
The reconnaissance campaign began with a sharp 500% increase in scanning activity on October 3, 2025, when researchers observed approximately 1,300 unique IP addresses probing Palo Alto login portals.
This initial surge already represented the largest burst of scanning activity in three months, with daily volumes previously rarely exceeding 200 IPs during the preceding 90-day period.
Palo Alto PAN-OS GlobalProtect Login Portals Surge
The escalating attack campaign demonstrates sophisticated coordination across geographically distributed infrastructure.
GreyNoise analysis reveals that 91% of the malicious IP addresses are geolocated to the United States, with additional clusters concentrated in the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Canada, and Russia.
Security researchers have identified approximately 12% of all ASN11878 subnets allocated to scanning Palo login portals, indicating significant infrastructure commitment to this operation.
The attack methodology suggests threat actors are systematically iterating through large credential databases, with login attempt patterns indicating automated brute-force operations against GlobalProtect SSL VPN portals.
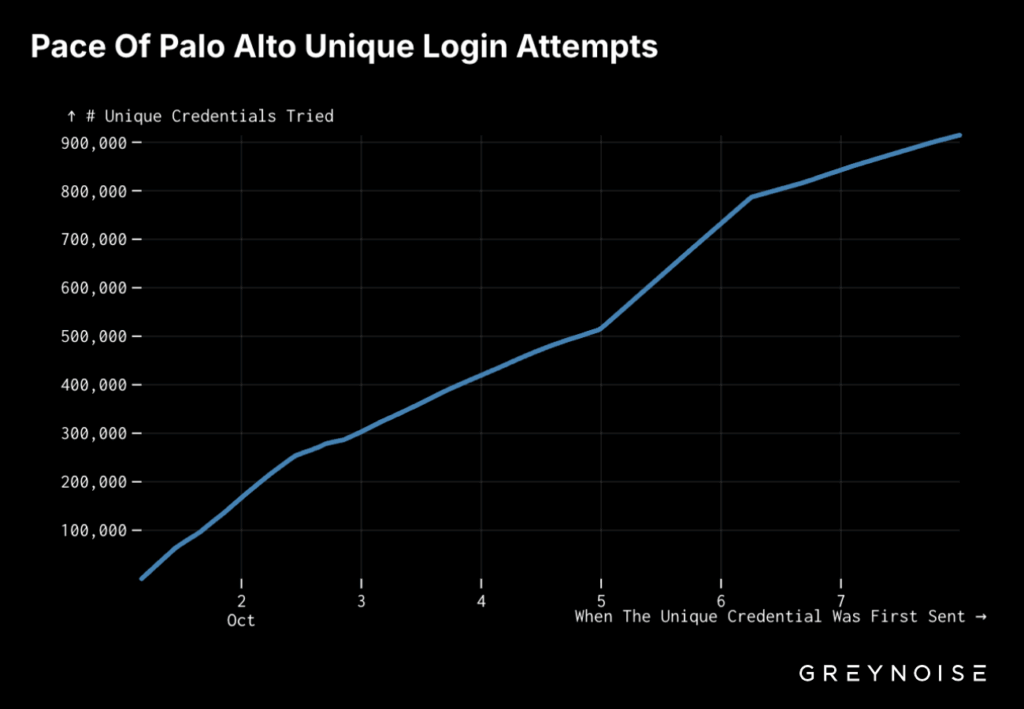
GreyNoise has published a comprehensive dataset containing unique usernames and passwords from Palo login attempts observed during the past week, enabling security teams to assess potential credential exposure.
Technical analysis reveals that 93% of participating IP addresses were classified as suspicious, while 7% received malicious designations.
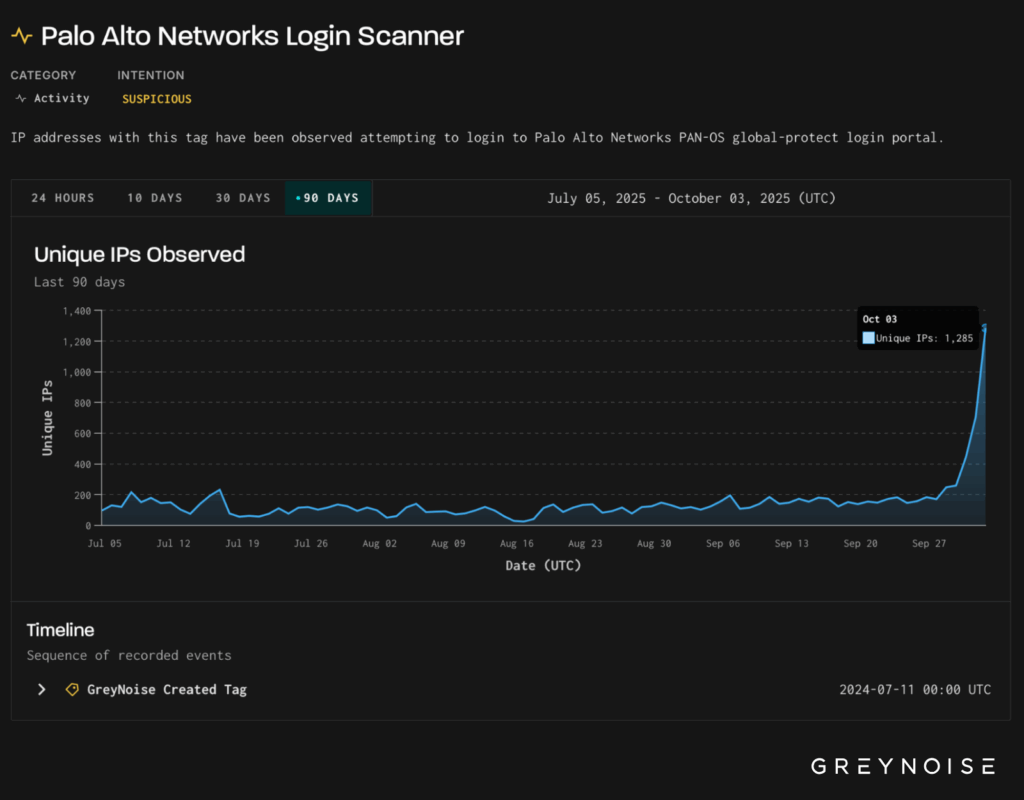
The scanning activity exhibits distinct regional clustering patterns with separate TCP fingerprints, suggesting multiple coordinated threat groups operating simultaneously.
Security researchers have identified potential correlations between the Palo Alto scanning surge and concurrent reconnaissance operations targeting Cisco ASA devices.
Both attack campaigns share dominant TCP fingerprints linked to infrastructure in the Netherlands, along with similar regional clustering behaviors and tooling characteristics.
The cross-technology targeting suggests a broader reconnaissance campaign against enterprise remote access solutions.
Concurrent surges observed across multiple remote access service platforms, though the exact relationship between these activities remains under investigation.
The targeted nature of these attacks is evident from their focus on GreyNoise’s emulated Palo Alto profiles, including GlobalProtect and PAN-OS systems.
This precision indicates attackers likely derived target lists from public reconnaissance platforms such as Shodan or Censys, or conducted their own fingerprinting operations to identify vulnerable Palo Alto devices.
Security teams should implement immediate defensive measures, including IP blocklisting of known malicious addresses, enhanced monitoring of GlobalProtect portal authentication logs, and implementation of additional access controls for remote VPN connections.
Cyber Awareness Month Offer: Upskill With 100+ Premium Cybersecurity Courses From EHA's Diamond Membership: Join Today
The post Attacks on Palo Alto PAN-OS Global Protect Login Portals Surge from 2,200 IPs appeared first on Cyber Security News.


