-
The cyber world never hits pause, and staying alert matters more than ever. Every week brings new tricks, smarter attacks, and fresh lessons from the field. This recap cuts through the noise to share what really matters—key trends, warning signs, and stories shaping today’s security landscape. Whether you’re defending systems or just keeping up, these highlights help you spot what’s coming
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
In the era of rapidly advancing artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud technologies, organizations are increasingly implementing security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure regulatory compliance. Among these measures, AI-SPM (AI Security Posture Management) solutions have gained traction to secure AI pipelines, sensitive data assets, and the overall AI ecosystem. These solutions help
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
A security flaw in Zabbix Agent and Agent2 for Windows has been discovered that could allow a local attacker to gain higher system privileges. The issue, tracked as CVE-2025-27237, stems from the way the agent loads its OpenSSL configuration file. By exploiting this weakness, an attacker with limited rights on a Windows host could escalate […]
The post Zabbix Agent/Agent2 for Windows Vulnerability Could Allow Privilege Escalation appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
Cybersecurity researchers have shed light on a Chinese-speaking cybercrime group codenamed UAT-8099 that has been attributed to search engine optimization (SEO) fraud and theft of high-value credentials, configuration files, and certificate data. The attacks are designed to target Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) servers, with most of the infections reported in India, Thailand
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
With the release of Kali Linux 2025.3, penetration testers and security professionals gain access to an innovative AI-powered assistant, the Gemini Command-Line Interface (CLI). This open-source package brings Google’s Gemini AI directly into the terminal, offering natural language–driven automation for common pentesting workflows. The integration of Gemini CLI marks a significant leap forward in the […]
The post Integrate Gemini CLI into Your Kali Terminal to Speed Up Pentesting Tasks appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
A remote code execution vulnerability affecting Google Chrome’s WebAssembly engine has been publicly disclosed, along with a fully functional exploit. The flaw, discovered and reported during TyphoonPWN 2025, involves a regression in the canonicalization logic for indexed reference types in WebAssembly and a novel sandbox bypass via JavaScript Promise Integration (JSPI). Researchers from SSD Secure […]
The post Technical Details and Exploit Released for Chrome Remote Code Execution Flaw appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
Researchers have published the full technical details and exploit code for a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in Google Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine.
Tracked internally as a WebAssembly type canonicalization bug, the flaw stems from an improper nullability check in the CanonicalEqualityEqualValueType function introduced by commit 44171ac in Chrome M135 and above.
This regression fails to distinguish between ref t0 and ref null t0, enabling an attacker to craft two recursive type groups that collide under the same MurmurHash64A hash value.
By launching a birthday attack on the type canonicalization, the exploit achieves nullability confusion on indexed reference types, undermining core Wasm type safety guarantees.
A novel V8 sandbox bypass leverages JavaScript Promise Integration (JSPI) state-switching flaws introduced in M137.
SSD Secure Disclosure stated that an attacker abuses an intra-state confusion in the secondary stack management logic to pivot execution between nested JS and Wasm stacks out of order.
By skipping over inactive stacks and spraying attacker-controlled values into suspended frames, the exploit gains full stack control and builds a return-oriented programming chain to invoke VirtualProtect on a RWX shellcode buffer.
Chrome RCE Vulnerability Exploit
The publicly released proof-of-concept comprises an HTML payload and accompanying JavaScript leveraging wasm-module-builder.js to generate bespoke Wasm types and functions. To deploy the exploit:
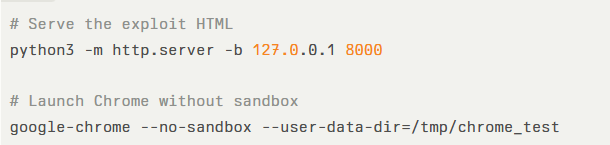
Then, navigate to http://127.0.0.1:8000/exp.html. Successful exploitation will spawn a Windows calc.exe process via a crafted ROP chain and RWX shellcode. The exploit script performs the following steps:
Enumerates two Wasm recursive type groups (t2null vs. t2nonnull) differing only in nullability, then uses a birthday attack across 2^32 MurmurHash64A values to locate a collision.
Casts a ref null t1 into ref t1, granting a sandboxed caged read/write primitive by abusing out-of-bounds access to a large ArrayBuffer.
Constructs nested promise-based Wasm exports to force stack switches, then exploits a missing SBX_CHECK in commit c6426203 to skip an inactive stack frame, yielding attacker-controlled execution context.
Sprays a retsled array of gadget addresses—pop rax; jmp rax, VirtualProtect thunk offsets, etc.—to mark shellcode memory as executable and jump into it.
Credit for the discovery and exploit goes to Seunghyun Lee (0x10n), winner of the Chrome RCE category at TyphoonPWN 2025.
A patch has been committed to address the nullability regression, reintroduce strict SBX_CHECKs in JSPI, and restore robust type safety in the V8 engine.
Users are strongly advised to update to Chrome M137.0.7151.57 (or later) as soon as possible to mitigate this critical RCE risk.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X for daily cybersecurity updates. Contact us to feature your stories.
The post Google Chrome RCE Vulnerability Details Released Along with Exploit Code appeared first on Cyber Security News.
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
Microsoft is set to roll out a highly anticipated multitasking feature for its Teams platform, which will allow users to open channels in separate windows.
This long-awaited update, scheduled for release in November, addresses one of the most common user requests and promises to improve workflow efficiency for millions of users significantly.
According to the Microsoft 365 Roadmap, the update, tracked as feature ID: 509110, will enable users to break free from the single-window interface that has defined channel-based collaboration.
Currently, users must constantly switch between different channels and chats within the main Teams application, a process that disrupts concentration and makes monitoring multiple conversations difficult.
This “context switching” is a well-known productivity killer, forcing users to reorient themselves each time they navigate to a new conversation.
The new feature will allow users to pop out a channel into its own dedicated window. This means a critical project channel, a team-wide announcements feed, or any other important conversation can remain persistently visible on a user’s screen, just like any other application window.
Enhancing Multitasking And Focus
The practical implications for daily productivity are substantial. With the ability to manage multiple windows, users can create a digital workspace that mirrors their specific needs.
For instance, a developer can keep a channel for technical discussions open on one monitor for quick reference while writing code in another.
A marketing professional can monitor a campaign launch channel for real-time updates while simultaneously collaborating on content creation in a separate chat.
This capability eliminates the need to constantly click back and forth, reducing mental friction and allowing for deeper focus on the task at hand.
By preventing important information from being hidden behind a click, the update ensures that users can stay informed without interrupting their primary workflow.
This new functionality builds upon the existing pop-out features already available in Microsoft Teams.
Users have long been able to separate individual chats, meetings, and calls into their own windows, and the absence of this capability for channels has been a conspicuous limitation.
The upcoming release finally addresses this gap, creating a more consistent and comprehensive multitasking environment across the entire platform.
Its introduction is a clear signal that Microsoft is actively listening to its user base and prioritizing fundamental usability enhancements.
As organizations continue to depend on digital collaboration hubs, this update is poised to be one of the most impactful quality-of-life improvements to Teams in recent years.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X for daily cybersecurity updates. Contact us to feature your stories.
The post Microsoft Teams Set to Introduce Highly Anticipated Multitasking Functionality appeared first on Cyber Security News.
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
Targeting Windows systems, Yurei employs advanced file encryption and stealth techniques to maximize impact and minimize detection. Encrypted files are appended with the extension .Yurei, and victims receive a ransom note named _README_Yurei.txt with Tor-based contact channels. CYFIRMA has observed a new ransomware strain, “Yurei Ransomware,” developed in Go language and circulating in multiple malware […]
The post Yurei Ransomware leverages SMB shares and removable drives to Encrypt Files appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
-
Cybercriminals have ramped up attacks on WordPress websites by stealthily modifying theme files to serve unauthorized third-party scripts. This campaign leverages subtle PHP injections in the active theme’s functions.php to fetch external code, effectively turning compromised sites into silent distributors of malicious ads and malware. The breach came to light when the site owner noticed […]
The post Hackers Exploit WordPress Sites by Silently Injecting Malicious PHP Code appeared first on GBHackers Security | #1 Globally Trusted Cyber Security News Platform.
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶
¶¶¶¶¶


