IBM published a security bulletin disclosing a serious Blind SQL injection vulnerability in its IBM Watsonx Orchestrate Cartridge for IBM Cloud Pak for Data, assigned CVE-2025-0165.
With a CVSS 3.1 base score of 7.6, this flaw could allow remote attackers with low privileges to compromise sensitive back-end databases by injecting malicious SQL statements.
Key Takeaways
1. Blind SQL injection in IBM Watsonx Orchestrate.
2. Caused by improper input sanitization.
3. Upgrade immediately—no workarounds.
Blind SQL Injection Vulnerability
The vulnerability originates from improper sanitization of user-supplied input in the Orchestrate Cartridge’s query processing engine.
Specifically, the cartridge fails to neutralize special SQL elements before concatenating them into dynamic queries, violating CWE-89: Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an SQL Command (‘SQL Injection’). An attacker who crafts a payload such as:
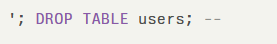
and submitting it through an exposed API endpoint could execute arbitrary SQL commands. This could enable the attacker to:
- Read confidential records
- Modify user permissions
- Delete critical data
- Insert malicious entries
The CVSS vector (CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:L/A:L) indicates network exploitability with low attack complexity and no user interaction, but requiring authenticated (low-privilege) access.
The vulnerability compromises confidentiality to a high degree, integrity to a low degree, and availability to a low degree.
Affected versions include IBM Watsonx Orchestrate Cartridge for Cloud Pak Data version 4.8.4–4.8.5 and 5.0.0–5.2.
| Risk Factors | Details |
| Affected Products | IBM watsonx Orchestrate Cartridge for IBM Cloud Pak for Data versions 4.8.4–4.8.5 and 5.0.0–5.2 |
| Impact | Read, add, modify, or delete backend database |
| Exploit Prerequisites | Authenticated low-privilege network access |
| CVSS 3.1 Score | 7.6 (High) |
Mitigations
IBM strongly urges all customers to upgrade to IBM Watsonx Orchestrate Cartridge version 5.2.0.1 immediately.
The patch enforces strict input validation and parameterized queries, effectively neutralizing malicious SQL tokens before execution. Detailed upgrade instructions are available in the IBM documentation.
Currently, there are no workarounds or temporary mitigations endorsed by IBM, making prompt patching critical. Organizations should also:
- Review database logs for anomalous query patterns
- Implement a Web Application Firewall (WAF) with SQL injection rules
- Enforce the principle of least privilege on service accounts
By addressing CVE-2025-0165 now, enterprises can safeguard their AI-driven orchestration workflows from unauthorized data manipulation and ensure compliance with organizational security policies.
Find this Story Interesting! Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant Updates.
The post IBM Watsonx Vulnerability Let Attackers Inject Malicious SQl Queries appeared first on Cyber Security News.



.webp)